Hardware Overview
Danger
ESD Sensitivity
The mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver is sensitive to ESD. Use a proper grounding system to make sure that the working surface and the components are at the same electric potential.
ESD Precaution
As recommended by the manufacturer, we highly recommend that users take the necessary precautions to avoid damaging their module. For example, users can utilize the iFixit Anti-Static Wrist Strap.

Active Antenna
Never inject an external DC voltage with the GNSS antenna, as it may damage the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver. For instance, when using a splitter to distribute the antenna signal to several GNSS receivers, make sure that no more than one output of the splitter passes DC. Use DC-blocks otherwise.
Introduction
-
SparkPNT GNSS Flex Module - mosaic-X5
SKU: GPS-28138

-
SparkPNT GNSS Flex modules are plug-in boards featuring different GNSS receivers. They are designed to be easily swapped for repairs and pin-compatible for upgrades. The boards have two 2x10-pin, 2mm pitch female headers connecting to carrier boards. For the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver, these pins will break out the USB, UART (x4), SD card, and Ethernet PHY interfaces, along with the PPS and event signals using a standardized pinout.
This SparkPNT GNSS Flex module features the Septentrio mosaic-X5, a compact, ultra-low power, multi-band, multi-constellation, high-precision GNSS receiver. The receiver supports the GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Beidou (China), Galileo (Europe), and NavIC (India) constellations, including regional systems (i.e. SBAS and QZSS). With its Real Time Kinematics (RTK) capabilities, the module can achieve a horizontal accuracy of 6mm (~0.25in), vertical accuracy of 1cm (~0.4in) using RTK, and timing precision of 5ns (5 billionths of a second). It also features Septentrio's unique AIM+ technology for interference mitigation and anti-spoofing, ensuring best-in-class reliability and scalable position accuracy.
The mosaic-X5 is a sophisticated module with an internal web server that can be utilized with any web browser. On the GNSS Flex module, the web server is accessed through either the USB data pins from the standard GNSS Flex headers; or the Ethernet PHY of the mosaic-X5, which is broken out on an third 2x10 pin, 2mm pitch female header. To guide users through the configuration options, Septentrio provides dozens of video tutorials about the web interface.
For the users who prefer a command-line interface, Septentrio has you covered. Users can still control and configure the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver through a CLI, which is useful for scenarios such as production line testing (in fact, that is how we test this board) or remote access.
mosaic-X5 Product Comparison
Below is a simple comparison table between our mosaic-X5 GNSS products and Septentrio's development and evaluation kits:
mosaic-X5 Development Kit
|
mosaic-go Evaluation Kit
|
mosaic-X5 GNSS Breakout
|
RTK mosaic-X5
|
mosaic-X5 Flex Module
|
SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS Antenna | Dual |
Single (mosaic-X5) Dual (mosaic-H) |
Single | Single | Single | Integrated |
| USB Connector | micro-B | micro-B | Type-C | Type-C | N/A* | Type-C |
| Ethernet |
Yes 10/100 Base-T |
No | No |
Yes 10/100 Base-T |
GNSS Flex Headers* | No |
| WiFi | No | No | No |
Yes - Network Bridge 10 Base-T |
No |
Yes - Network Bridge 10 Base-T |
| Tilt Compensasion | No | No | No | No | Yes* | No |
| COM Ports | 4 | 2 | 4 |
1 - mosaic-X5 1 - ESP32 |
4 |
1 - mosaic-X5 1 - ESP32 |
| µSD Card Slot | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GNSS Flex Headers* | Yes |
| Reset/Log Buttons | Yes | No* | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Logic-Level |
1.8V 3.3V |
3.3V | 3.3V |
3.3V 5V |
3.3V | 3.3V |
| PPS Signal | Header Pin | 6-Pin JST Connector | SMA Connector | Screw Terminal | GNSS Flex Headers* | No |
| Enclosure Material | N/A | Metal | N/A | Aluminum | N/A | Plastic |
| Dimensions | N/A | 71 x 59 x 12mm ± 1mm | 70.9 x 50.8 x 8mm |
180.6 x 101.8 x 41mm Enclosure Only |
44.5mm x 31.8mm x 10.4mm | |
| Weight | N/A | 58g ± 1g | 22.6g |
415.15g Enclosure Only |
GNSS Only: 14.0g IMU: 15.2g |
mosaic-go Evaluation Kit
The reset pin is exposed on 4-pin JST connector and the log pin is connected to the latch pin of the SD card slot.
mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex Modules
SparkPNT GNSS Flex modules are modular, plug-in boards that utilize a carrier board to access the pins of the GNSS Flex headers.
- The GNSS only variant of the SparkPNT GNSS Flex module includes a middle header that breaks out the Ethernet PHY interface of the mosaic-X5.
- The IMU variant of the SparkPNT GNSS Flex module includes the IM19 IMU for RTK tilt-compensation applications with the mosaic-X5.
Design Files
-
Design Files
- Schematic
- KiCad Files
- STEP File
- Board Dimensions:
- 1.75" x 1.25" (44.45mm x 31.75mm)
-
Manipulate 3D Model
Controls Mouse Touchscreen Zoom Scroll Wheel 2-Finger Pinch Rotate Left-Click & Drag 1-Finger Drag Move/Translate Right-Click & Drag 2-Finger Drag 
Dimensions of the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module. Need more measurements?
For more information about the board's dimensions, users can download the KiCad files for this board. These files can be opened in KiCad and additional measurements can be made with the measuring tool.
KiCad - Free Download!
KiCad is free, open-source CAD program for electronics. Click on the button below to download their software. (*Users can find out more information about KiCad from their website.)
Measuring Tool
This video demonstrates how to utilize the dimensions tool in KiCad, to include additional measurements:

Board Layout
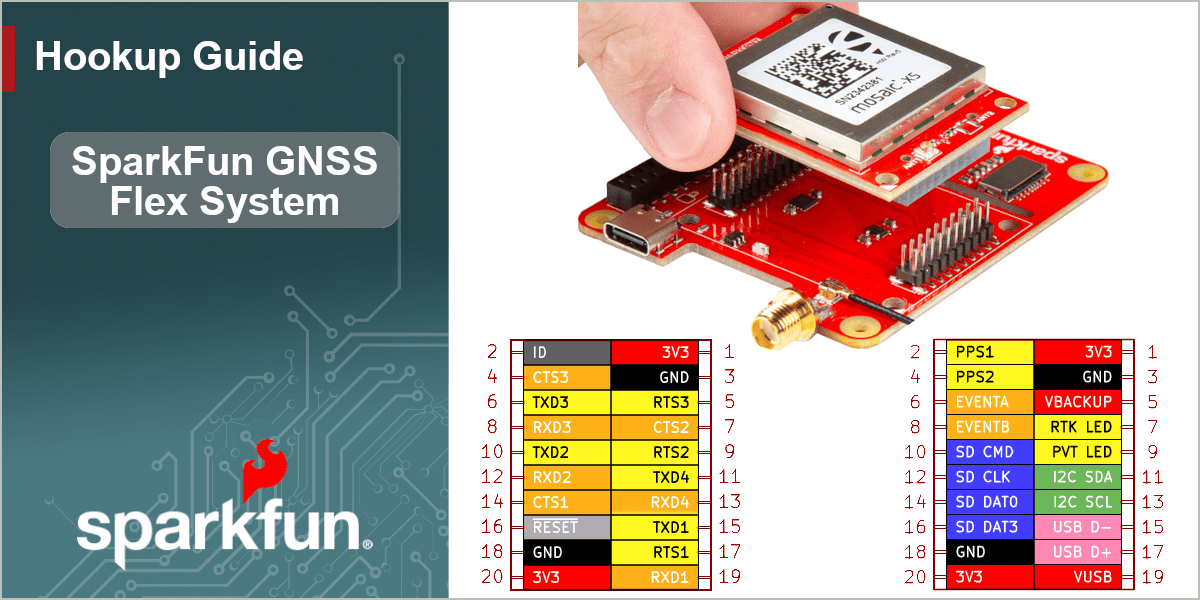
The GNSS Flex system is designed around two 2x10-pin, 2mm pitch headers used to mate the two types of boards. A standardized pin layout, keeps the ecosystem pin-compatible for upgrades and allows boards to be easily swapped for repairs. Depending on the capabilities of the GNSS receiver, these pins will breakout the USB, UART (x4), I2C, and SD card interfaces along with any PPS or event signals of the GNSS receiver.
The mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module has the following features:
-
- mosaic-X5 GNSS Receiver
- The Septentrio mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver
-
- GNSS Flex Headers
- Two sets of 2x10 pin, 2mm pitch female headers for connecting a GNSS Flex module to carrier boards
-
- Ethernet PHY Header
- A 2x10 pin, 2mm pitch female header that breaks out the Ethernet PHY pins of the mosaic-X5
-
ANT1U.FL Connector- An U.FL connector for attaching an external GNSS antenna
mosaic-X5 GNSS Receiver
The centerpiece of the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module, is the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver from Septentrio. Their mosaic modules are low-power, multi-band, multi-constellation GNSS receivers capable of delivering centimeter-level precision at high update rates. The modules also feature Septentrio's unique AIM+ technology for interference mitigation and anti-spoofing, which ensures their best-in-class reliability and scalable position accuracy.
Features:
- Operating Voltage: 3.135 - 3.465V
- Operating Temperature: -40 - 85°C
- GNSS Support
- GPS: L1C/A, L1PY, L2C, L2P, L5
- GLONASS: L1CA, L2CA, L2P, L3 CDMA
- Beidou: B1I, B1C, B2a, B2b, B2I, B3
- Galileo: E1, E5a, E5b, E5 AltBoc, E6
- QZSS: L1C/A, L1 C/B, L2C, L5
- Navic: L5
- SBAS: Egnos, WA
- Antenna Specifications
- Preamplification Range: 15-50dB
- Bias Voltage: 3.0 - 5.5V
- 448 Hardware Channels
- Update Rate: 100Hz
- Latency: < 10ms
- Time to Fix
- Cold Start: < 45s
- Warm: < 20s
- Reacquisition: 1s
- Timing Precision: 5ns
-
Position Accuracy
Correction Horizontal Vertical RTK 0.6cm (±0.5ppm)
~0.25"1cm (±1ppm)
~.4"DGNSS 40cm
~1.3'70cm
~2.3'SBAS 60cm
~2'80cm
~2.6'Standalone 1.2m
~4'1.9m
~6.2'
Info
The mosaic-X5 has three power modes: Active, Standby, and Off (see the Power Modes section).
Power Modes
The mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver operates in three different power states.
- Off - The module is completely turned off
- When transitioning to the Off state from Active, recent data may not be lost and not logged to the external SD card
- Standby - The module is in a low-power consumption mode (1)
- The module power consumption in standby is <5mW
- The
PMIC_ON_REQpin is drivenLOW - The
MODULE_RDYpin is in aLOW - Monitors the state of the
ONOFFpin (Not available)
- Active - The module is operating with all functions active
- On power up, the module restarts in the configuration stored in the boot configuration file
- The
PMIC_ON_REQpin is drivenHIGH - The
MODULE_RDYpin is in aHIGH(2)
- Essentially, the same state as Off; except in the transition to the Standby mode, before the module shuts down:
- All logging tasks are terminated
- The SD card is unmounted
- The
PMIC_ON_REQpin is drivenLOW
- Level becomes
HIGHabout 300ms after powering up, reset, or waking up from standby
Info
By default, the board is hardwired to operate only in the Active and Off modes.
For more information on the power management of the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver, please refer to sections 3.4, 3.5, 4.1, and 4.13 of the hardware manual.
Enabling Standby Mode
Users can enable Standby mode on the mosaic-X5, by modifying the V_BATT jumper (see the Jumpers section) and providing an external power source for the V_BATT pin (3.3V). However, because the ONOFF pin isn't exposed users will need to power cycle the board to return to the Active state.
Drive Current - PMIC_ON_REQ/MODULE_RDY
The drive current on the PMIC_ON_REQ and MODULE_RDY pins is low. Enough to be read by a digital pin on a microcontroller, but not high enough to drive an LED.
Power Consumption
The power consumption of the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver depends on the GNSS signals enabled and the positioning mode. The table below, lists the average power consumption for common configurations. The current listed, is based on a supply voltage of 3.3V.
| GNSS Signals | Positioning Mode | Power (mW) | Current (mA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS L1 C/A | Stand-Alone (1Hz) | 550 | 167 |
| GPS L1/L2 | RTK (1Hz) | 670 | 203 |
| GPS/GLONASS L1/L2 | RTK (1Hz) | 695 | 211 |
| GPS/GLONASS L1/L2+GALILEO L1/E5a +BeiDou B1C/B2a | RTK (1Hz) | 850 | 258 |
| GPS/GLONASS L1/L2+GALILEO L1/E5a +BeiDou B1C/B2a | RTK (100 Hz) | 930 | 282 |
| GPS/GLONASS L1/L2 + L-band | PPP (1Hz) | 760 | 230 |
| All signals from all GNSS constellations | Static (1Hz) | 910 | 276 |
| All signals from all GNSS constellations +L-band | Static(1Hz) | 980 | 297 |
| All signals from all GNSS constellations +L-band | Static (100Hz) | 1080 | 327 |
Source: mosaic-X5 Hardware Manual
Frequency Bands
The mosaic modules are multi-band, multi-constellation GNSS receivers. Below, are charts illustrating the frequency bands utilized by all the global navigation satellite systems and the ones supported by the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver.
The frequency bands supported by the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver.
Frequency bands of the global navigation satellite systems. (Source: Tallysman)
Info
For a comparison of the frequency bands supported by the mosaic modules, refer to section 3.1 of the hardware manual.
What are Frequency Bands?
A frequency band is a section of the electromagnetic spectrum, usually denoted by the range of its upper and lower limits. In the radio spectrum, these frequency bands are usually regulated by region, often through a government entity. This regulation prevents the interference of RF communication; and often includes major penalties for any interference with critical infrastructure systems and emergency services.

However, if the various GNSS constellations share similar frequency bands, then how do they avoid interfering with one another? Without going too far into detail, the image above illustrates the frequency bands of each system with a few characteristics specific to their signals. Wit these characteristics in mind, along with other factors, the chart can help users to visualize how multiple GNSS constellations might co-exist with each other.
For more information, users may find these articles of interest:
Position Accuracy
The accuracy of the position reported from the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver, can be improved based upon the correction method being employed. Currently, RTK corrections provide the highest level of accuracy; however, users should be aware of certain limitations of the system:
- RTK technique requires real-time correction data from a reference station or network of base stations.
- RTK corrections are signal specific (i.e. an RTK network might provide corrections on only
E5band notE5a).
- RTK corrections are signal specific (i.e. an RTK network might provide corrections on only
- The range of the base stations will vary based upon the RTK method being employed.
- The reliability of RTK corrections are inherently reduced in multipath environments. However, with Septentrio's multipath mitigation technology (APME+) on the mosaic-X5, these errors are significantly reduced when compared to multipath mitigation techniques that modify the correlators in the tracking channels.
RTK Corrections
To understand how RTK works, users will need a more fundamental understanding of the signal error sources.
Tip
For the best performance, we highly recommend that users configure the module to utilize/provide RTK corrections with a compatible L1/L2/L5/L6 GNSS antenna and utilize a low-loss cable.
GNSS Flex Headers
The GNSS Flex system is designed around two 2x10-pin, 2mm pitch headers used mate the two types of boards. A standardized pin layout, keeps the ecosystem pin-compatible for upgrades and allows boards to be easily swapped for repairs. For the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver, these pins will breakout the USB, UART (x4), and SD card interfaces along with a configurable PPS signal, two event signals, and two LED status indication signals from the GNSS receiver.
Below, are the features that are available from the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver.
Supported Interfaces:
- 4x UART (LVTTL, up to 4 Mbps)
- Ethernet (RMII/MDIO), 10/100 Mbps (1)
- USB device (2.0, HS)
- SDIO (mass storage)
2x GPIO user programmable(2)- 2x LED outputs
- 2x Event markers
- 1x Configurable PPS out
- Broken out on the extra middle header
- Not available on the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.
For most users, this will be the primary interface for the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver.

- When a module is initially connected to a computer, the board will initialize as a USB mass storage device.
- For Windows PCs, the USB driver (1) can be installed from the mass storage device or the RxTools software suite.
- When the SD card is mounted, this drive will contain the contents of the SD card that is inserted on the board.
- Once the USB driver is installed:
- Two virtual
COMports are emulated, which can be used as standardCOMports to access the receiver. - This interface will support Ethernet-over-USB.
- By default, the receiver is not allowed to access the Internet over USB.
- The IP address allocated to the Ethernet-over-USB interface is
192.168.3.1.- The IP address cannot be changed; therefore, only single receiver should be connected to your computer at a time.
- Two virtual
- On Linux, the standard Linux CDC-ACM driver is suitable.
The mosaic-X5 has four UARTs ports, which can be operated and configured separately.

COMports 1-3 feature flow control pins, which are disabled by default.- These ports also support a point-to-point protocol server, by which it can accept TCP/IP connections over a serial link.
Default Configuration
By default, the UART ports are configured with the following settings:
- Baudrate: 115200bps
- Data Bits: 8
- Parity: No
- Stop Bits: 1
- Flow Control: None
From the module, the PPS output signal's logic-level is 1.8V. However, for the convenience of users, we have added a buffer and bumped up the signal's logic-level to 3.3V on the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.

PPS signal's output on the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.
Use Case
- Users could use this signal in conjunction with the event pins to synchronize two mosaic-X5 GNSS receivers with each other.
- Users could use this signal to create their own Stratum 0 source for the NTP on a primary time server.
The data logging functionality of the board can be configured through the software/web interfaces.
Initial Configuration
Before data logging can occur, it is necessary to create a logging stream from the Logging tab of the web interface or using the RxTools software suite. Streams can contain NMEA or SBF (Septentrio Binary Format) data; SBF can contain RTCM and/or RINEX.
SD Card Specifications
The mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver is only compatible with SD cards of up to 32GB, formatted with a FAT32 file system.
Standby Mode
When Standby mode is initialized, the module terminates all running processes and unmounts the external SD card to avoid any log file corruption (see the Power Modes section).
The mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver features two general purpose, output LED pins. These pins have a maximum output current of 10 mA and output impedance of 20Ω.
The mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver features two general purpose, event input pins. These pins can be used to time tag external events with a time resolution of 20ns.

Tip
For example, these pins can be used in conjunction with the PPS output signal for time syncing.
Extra Header
In addition to the GNSS Flex headers, an extra 2x10 pin, 2mm pitch female header is populated between them. This header breaks out the Ethernet PHY interface, along with a few other operation indication signals.
The JST connector on the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.
-
- RMII Interface
- The module supports an Ethernet PHY through its RMII interface. An up-to-date list of supported PHY's can be found in Septentrio’s Knowledge Base.
-
PMIC_ONPin- The state of
PMICpin indicates when the subsystems are energized and ready (see the Power Modes section).
-
READYPin- The
RDYpin indicates the operational mode of the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver (see the Power Modes section). The level is high when module is operating, and low when in standby or reset.
-
ON_OFFPin- The
RDYpin indicates the operational mode of the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver (see the Power Modes section). The level is high when module is operating, and low when in standby or reset.
U.FL Connector
Users will need to connect a compatible GNSS antenna to the ANT1 U.FL connector. The type of antenna used with the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver affects the overall accuracy of the positions calculated by the GNSS receiver.
- Passive antennas are not recommended for the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver.
-
There is no need to inject an external DC voltage for the GNSS antenna. Power is already provided from the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver for the LNA of an active antenna.
Danger
Never inject an external DC voltage into the SMA connector for the GNSS antenna, as it may damage the mosaic-X5 GNSS receiver. For instance, when using a splitter to distribute the antenna signal to several GNSS receivers, make sure that no more than one output of the splitter passes DC. Use DC-blocks otherwise.
The U.FL connector to attach an external GNSS antenna to the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.
Tip
For the best performance, we recommend users choose a compatible L1/L2/L5/L6 GNSS antenna and utilize a low-loss cable. Also, don't forget that GNSS signals are fairly weak and can't penetrate buildings or dense vegetation. The GNSS antenna should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
Jumpers
There are two jumpers on the back of the board that can be used to easily modify the hardware connections on the board.
The jumpers on the back of the mosaic-X5 GNSS Flex module.
Never modified a jumper before?
Check out our Jumper Pads and PCB Traces tutorial for a quick introduction!
















