Introduction
-
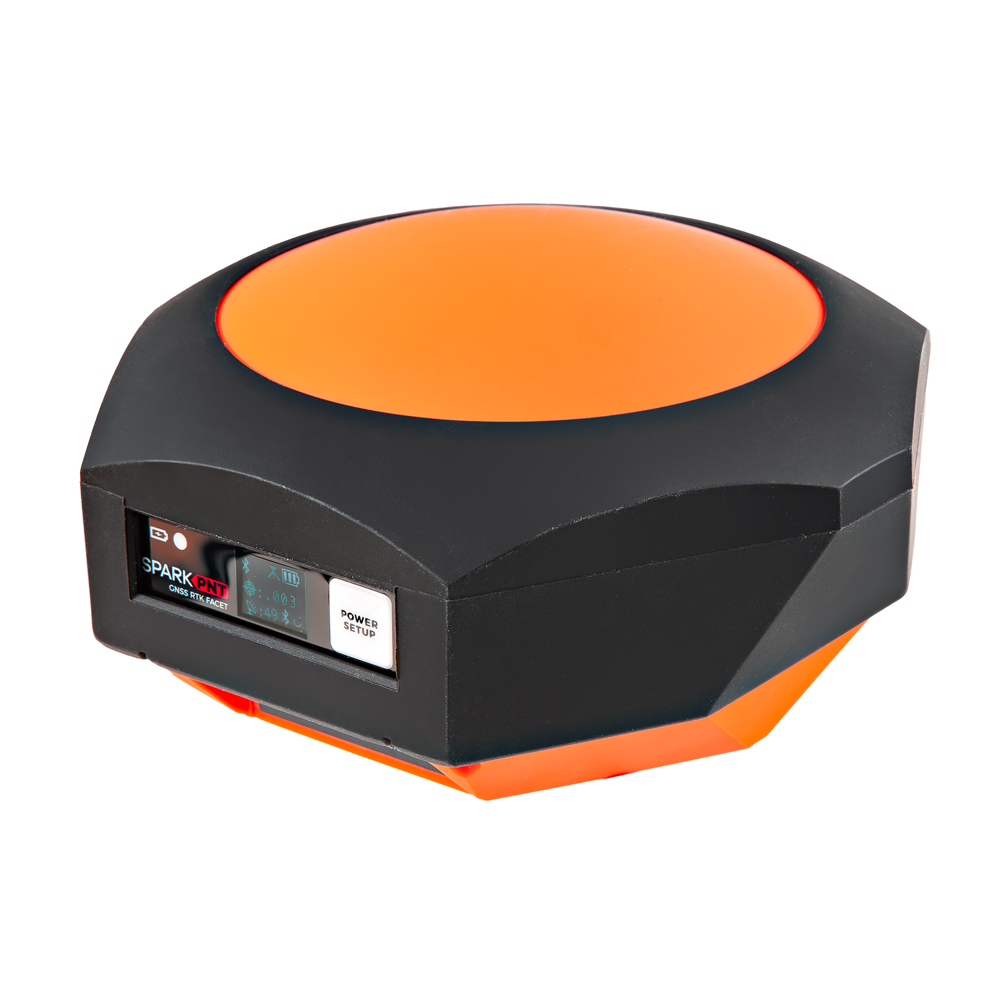
SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic
SKU: GPS-29688


-
Designed and manufactured in Boulder, Colorado, USA, and utilizing the multi-band mosaic-X5 from Septentrio, the SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic is the top of the line receiver for high precision geolocation and surveying needs. For basic users, it's incredibly easy to get up and running; for advanced users, the RTK Facet mosaic is a flexible and powerful tool. With just the press of a button, the RTK Facet mosaic is the fastest way to take centimeter-grade measurements. With a subscription to the PointPerfect Flex NTRIP/RTCM service or any other correction service, 10mm Real Time Kinematic fixes are less than a minute away. By connecting your phone to the RTK Facet mosaic over Bluetooth®, your phone or tablet can receive the NMEA output and work with most GIS software programs. This is exactly how $10,000 surveying devices have been operating for the past decade - we just made it faster, more precise, and a lot more economical.
The RTK Facet mosaic works with common GIS software for Android and iOS including SW Maps Android / iOS, Field Genius, SurvPC, Survey Master, Vespucci, QGIS, QField, and any GIS software that supports NMEA over Bluetooth.
Under the hood of the SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic is an ESP32-WROVER-E connected to a mosaic-X5 GNSS multi-band receiver, and a variety of peripheral hardware (LiPo fuel gauge, microSD, etc). Additionally, housed under the dome of the RTK Facet mosaicis a surveyor grade L1/L2/L5 antenna. This antenna is a unique combination of elements designed to receive the GNSS signals (L1/L2/L5). The RTK Facet mosaic is programmed in Arduino and can be tailored by you to fit whatever your needs may be.
This device can be used in five modes:
- GNSS Positioning (~30cm accuracy) - also known as Rover
- GNSS Positioning with RTK (1.4cm accuracy) - also known as Rover with RTK Fix
- GNSS Base Station
- GNSS Base Station NTRIP Server
At Power On the device will enter Rover or Base mode; whichever state the device was in at the last power down. When the POWER/SETUP button is pressed momentarily, a menu is presented to change the RTK Facet mosaic from Rover to Base mode or vice-versa. The display will indicate the change with a small car (Rover) or flag (Base) icon.
In Rover mode the RTK Facet mosaic will receive
L1,L2, andL5GNSS signals from the four constellations (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou). The device will calculate the position based on the combination of GNSS. If the device has been registered with PointPerfect or any other correction service, the receiver will quickly (within 60 seconds) obtain an RTK float, then fix. Similar to a standard grade GPS receiver, the RTK Facet mosaic will output industry standard NMEA sentences at 4Hz and broadcast them to any paired Bluetooth® device. The end user will need to parse the NMEA sentences using commonly available mobile apps, GIS products, or embedded devices (there are many open source libraries). Unlike standard grade GPS receivers that have 2500mm accuracy, the accuracy in this mode is approximately 10 to 60mm horizontal positional accuracy.In Base mode the device will enter Base Station mode. This is used when the device is mounted to a fixed position (like a tripod or roof). The RTK Facet mosaic will initiate a survey. After 60 to 120 seconds the survey will complete and the RTK Facet mosaic will begin transmitting RTCM correction data out the radio port. A base is often used in conjunction with a second RTK Facet mosaic (or RTK Torch, Facet, Surveyor, Express, Express Plus, etc) unit set to Rover to obtain the 10mm accuracy. Said differently, the Base sits still and sends correction data to the Rover, so that the Rover can output really accurate position data for its location.
In addition to supplying position data, the RTK Facet mosaic is capable of logging NMEA and raw GNSS satellite data for post processing making it ideal for research and advanced positioning applications.
The RTK Facet mosaic is an open-source hardware product meaning you can fully obtain, see, and even modify the electrical and mechanical design files. This allows for easier maintenance and repair over time.
The SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic kit includes everything you need: the enclosed device, thread adapter, charger, data cables, and carrying case. It does NOT include a surveying pole (any additional items will need to be purchased separately).
Permanent Installation
The SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic is not designed for permanent outdoor mounting. Please use the RTK mosaic-X5 or the RTK Reference Station that is located inside or protected from the elements. Or, for a DIY solution, the ESP32 attached to our ZED-F9P breakout is a great way to go. See our How to Build a DIY GNSS Reference Station tutorial for more information.
Completely Open-Source
- The RTK Everywhere firmware is open-source, so users can obtain, check, and even modify the device's functionality. This allows for easier feature expansion, bug maintenance, and longer device longevity.
- Additionally, the hardware is also open-source, so users can obtain, check, and even modify the device's design.
Required Materials
To get started, users will need a few items. Some users may already have a few of these items, feel free to adjust accordingly.
- Computer or mobile device with Bluetooth® and WiFi capabilities
- SparkPNT RTK Facet mosaic
- Telescopic Surveying Pole
- PointPerfect Registration
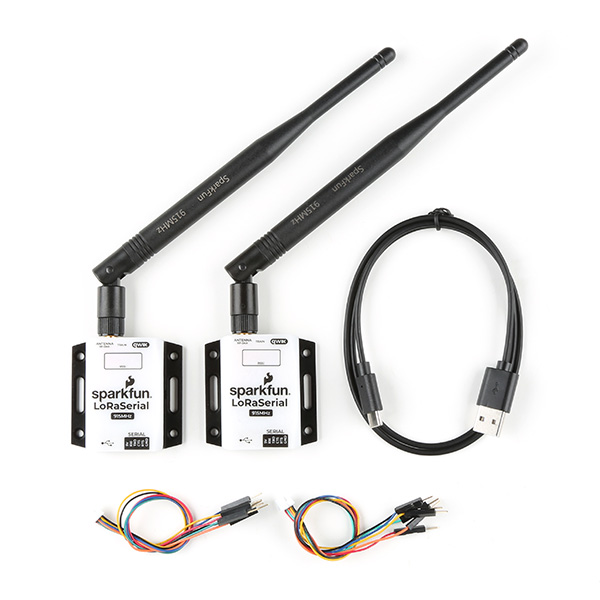
Serial Transceivers, UART Adapters, and USB Cables
To configure the UART ports that are broken out on the board, users will need a UART adapter. Once configured, the UART ports can utilize one of our RF transceivers to send/receive RTCM messages.
Jumper Modification
To modify the jumpers, users will need soldering equipment and/or a hobby knife.
New to jumper pads?
Check out our Jumper Pads and PCB Traces Tutorial for a quick introduction!
Suggested Reading
As a more sophisticated product, we will skip over the more fundamental tutorials (i.e. Ohm's Law and What is Electricity?). However, below are a few tutorials that may help users familiarize themselves with various aspects of the board.
Tip
Check out the www.gps.gov website to learn more about the U.S.-owned Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) of other countries.
 Purchase from SparkFun
Purchase from SparkFun